
Bei der Anschaffung einer neuen Reinigungsanlage geben oft die Investitionskosten den Ausschlag, zum Beispiel bei der Wahl der Verfahrenstechnik oder der Ausstattung. Folgekosten müssen jedoch ebenfalls berücksichtigt werden.
Ressourceneffizienz als Teil der Life Cycle Kostenbetrachtung
Energieaufwand für die Verdampfung von offenen Bädern
Je m² Badoberfläche in Abhängigkeit von der Temperatur
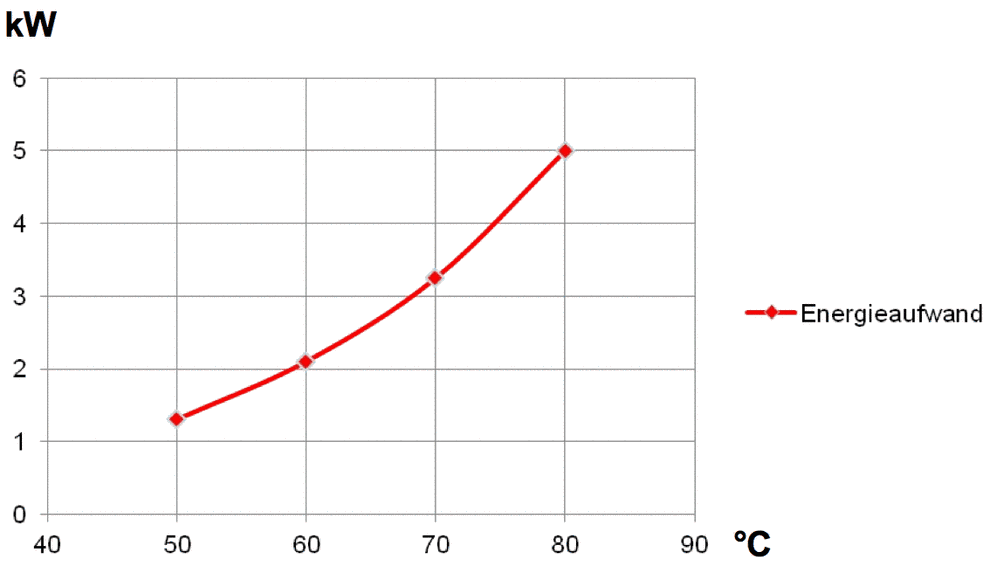
Bei 80 °C beträgt die durchschnittliche Heizleistung ca. 8 kW. Davon sind allein ca. 60 % bedingt durch die reinen Verdampfungsverluste. Der Rest wird somit durch den Energiebedarf der zu behandelnden Werkstücke sowie der allgemeinen Wärmeverluste beeinflusst.
Wasserverlust von offenen Bädern
Je m² Badoberfläche in Abhängigkeit von der Temperatur
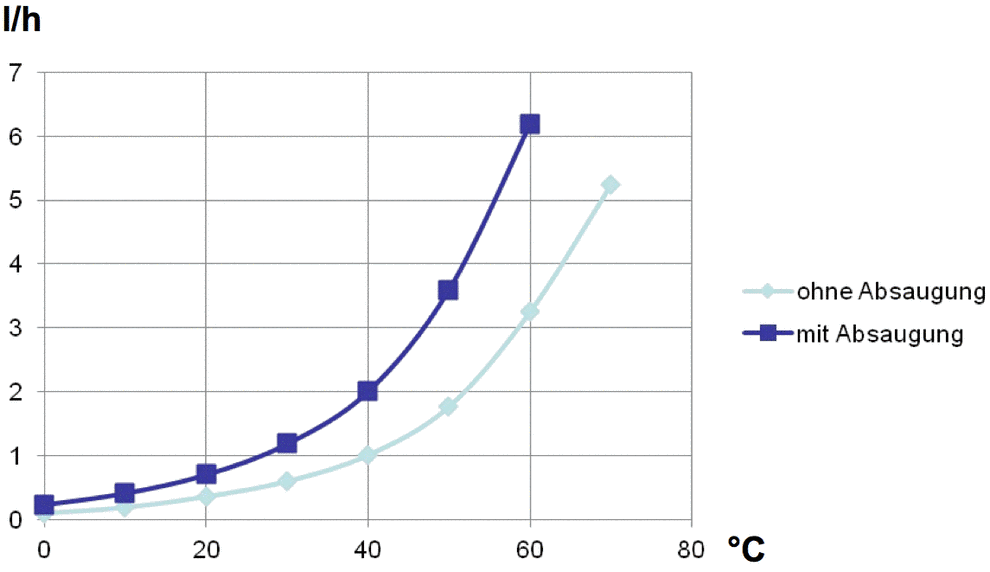
Bei offenen Badanlagen wird zudem der Wasserverlust erheblich von der Temperatur und der notwendigen Absaugleistung beeinflusst.
Anlagensysteme im Energieeffizienzvergleich
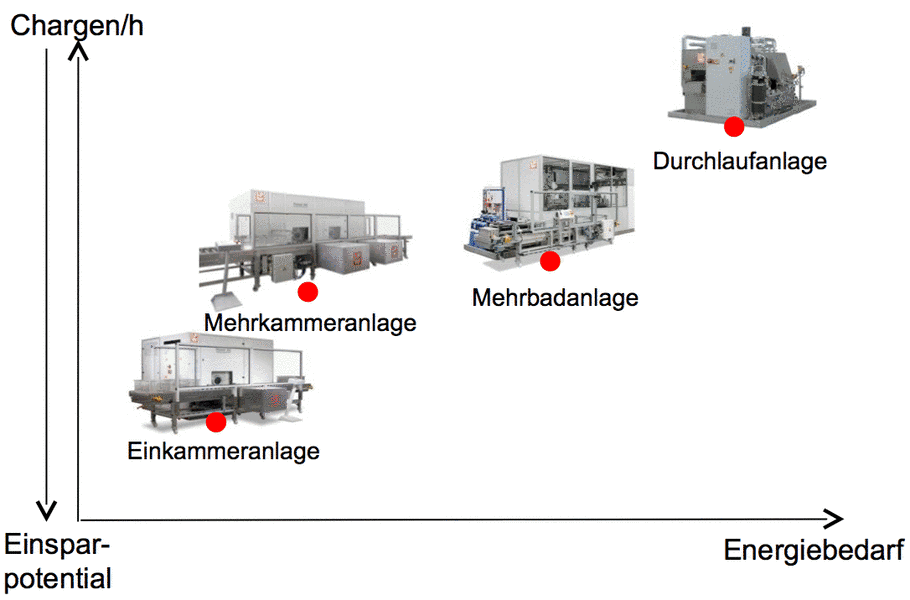
Die Auswahl des Anlagentyps entscheidet im Wesentlichen die Betriebskosten unter dem Aspekt der Energieeffizienz.
Vergleich des Energieverbrauchs
Ohne Berücksichtigung der Effekte durch Neuansatz eines Reinigungsbades, zeigt sich die wässrige Einkammeranlage als das effizientere System mit den größten Effizienzsteigerungsmöglichkeiten. Als Doppelkammeranlage verstärkt sich dieser Effekt durch die Verteilung der Grundlast auf einen höheren Durchsatz.
| Einkammeranlage Kohlenwasserstoff | Einkammeranlage wässrig | Doppelkammeranlage wässrig | Reihentauchanlage wässrig | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leistungsaufnahme Volllastbetrieb (kW) |
33,5 | 27,5 | 45,0 | 91,0 |
| Max. Durchsatz (Chargen/h) | 5(Taktzeit 12 min) | 5(Taktzeit 12 min) | 9(Taktzeit 6,5 min) | 13,3(Taktzeit 4,5 min) |
| Energiebedarf (kWh/Charge) | 6,7 | 5,5 | 5,0 | 6,8 |
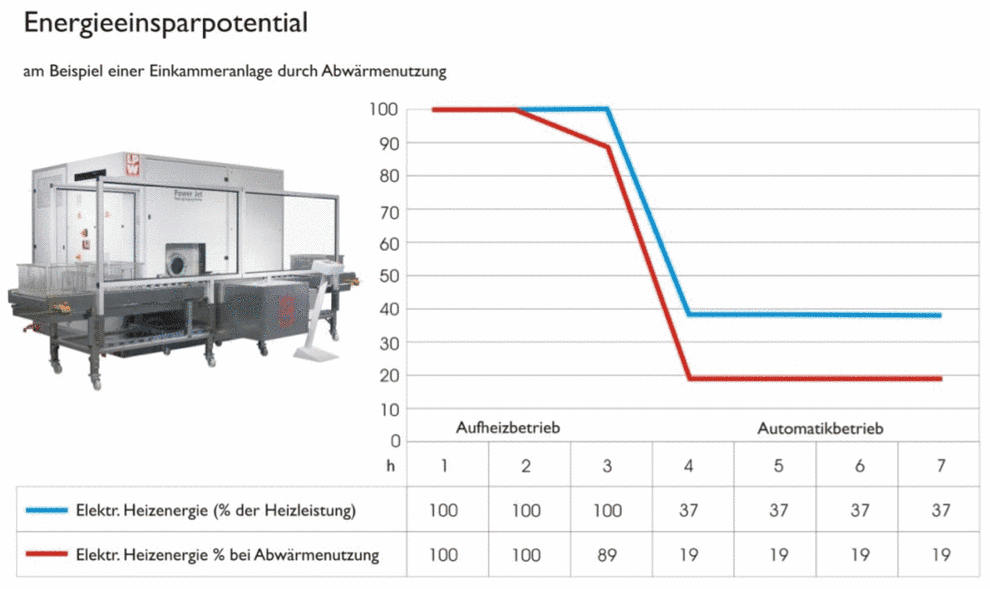
Ein Beispiel zur Energieeinsparung
Spezielle Fachbeiträge zur weiteren Information:
- Auf dem Weg zum „Industrial Clean Management“ Teil 1
- Auf dem Weg zum „Industrial Clean Management“ Teil 2
- TCO: Bei Investitionen Folgekosten betrachten
- Herausforderung Clean Management
- Energieeffizienz: Schritt für Schritt weniger Energie
- Weniger Kosten durch lange Badstandzeiten
- Bäderheizen mit Solarthermie
